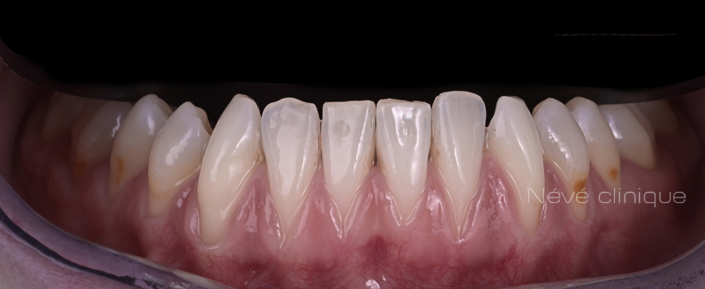
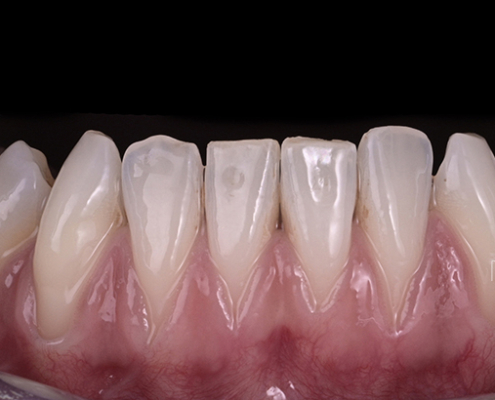
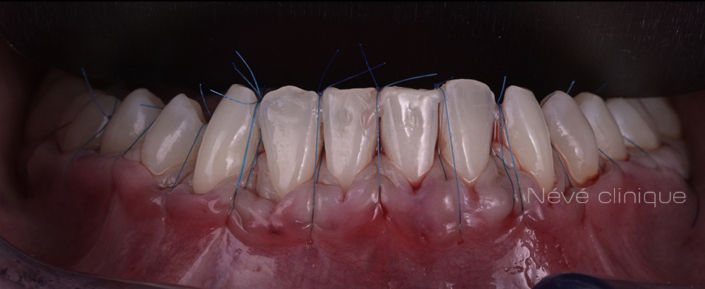
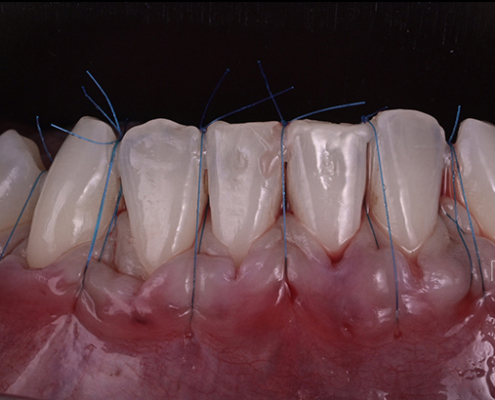
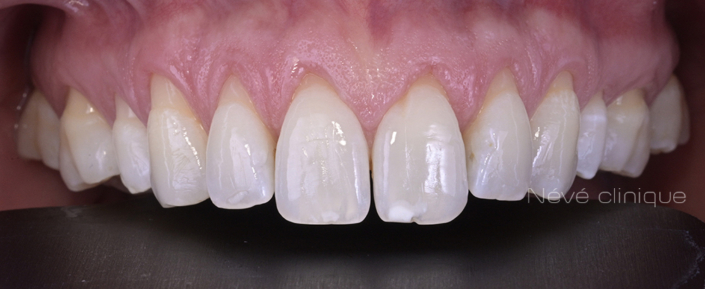
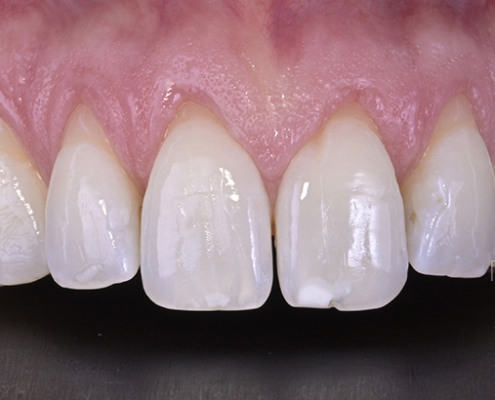
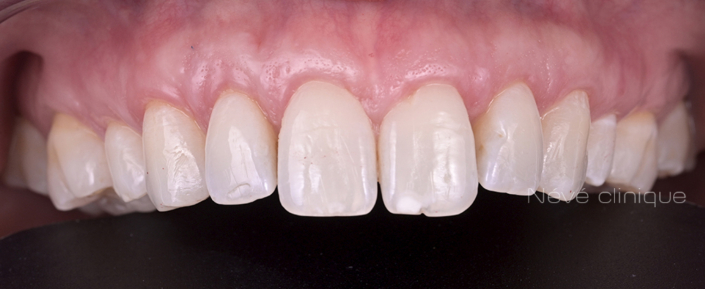
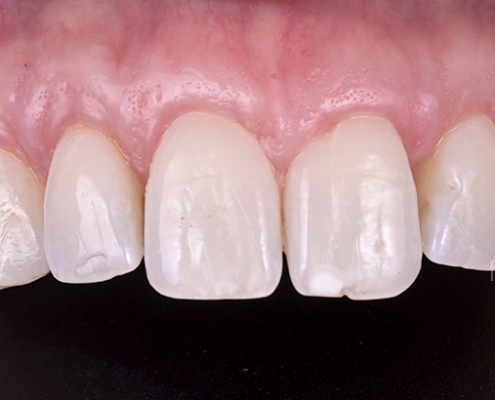
Gum graft
Periodontal plastic surgery procedure.
Periodontal plastic surgery or mucogingival surgery involves techniques aimed at improving the soft tissues: the gums.
Mucogingival surgery encompasses various gingival grafting techniques.
These techniques are often used to treat gingival recessions.
What is gum recession?
A gingival recession is a retraction of the gum, a localized destruction of the gum that covers the dental root.
What are the causes of gum recession?
Gingival recessions result from multiple factors. Indeed, several elements contribute to their occurrence.
Favoring factors
First of all, several conditions can promote gingival recessions:
- Thin and weakly keratinized gums
- Low height of keratinized tissue
- Dental malposition
- Proximity of the labial frenulum
Triggering factors
In addition to the favoring factors, certain elements can trigger gingival recessions:
- Gingival inflammation
- Mechanical aggressions due to inappropriate and too vigorous brushing
- Certain dental movements performed during orthodontic treatments
- Jewelry such as piercings
- Inadequate dental care
- Onychophagia, which is nail biting
- Eating disorders such as bulimia and anorexia
By understanding these factors, we can better prevent and treat gingival recessions.
What are the consequences of gum recession?
Reduction of protection:
The gum plays a crucial role as a barrier and protector for the bone. When the gum recedes, it becomes thinner and often less protective. The underlying bone also recedes, leading to a loss of tooth support. Additionally, hygiene becomes more complicated due to difficult access and increased sensitivity, thus raising the risk of periodontal disease.
Tooth sensitivity:
When the gum recedes, it exposes the root of the tooth which is no longer protected. This situation can cause increased sensitivity to cold, heat, or sweet foods.
Root erosion:
Without the protection of the gum, the root is exposed to mechanical, bacterial, and chemical stress. This exposure can lead to erosion and partial destruction of the root.
Elongated tooth:
Visually, gum recession exposes more of the root, giving the impression that the teeth are elongated. In reality, the length of the tooth remains unchanged; the issue stems from the position of the gum.
What are the treatments for gum recession?
We primarily treat gingival recessions through surgical interventions. To cover the recession, we move the gingival tissues and add gum (graft) to correct the thickness.
Advancement of techniques
Techniques have significantly evolved in recent years. Today, we use micro-surgery interventions that are minimally invasive. These methods generally provide more aesthetic and reliable results, with minimal pain.
Post-operative comfort
Thanks to these techniques, post-operative pain is usually classified as discomfort only.
What are the different grafting techniques?
We use numerous techniques and variations for gum grafts, but two main techniques stand out:
The epithelial-connective tissue graft
For this technique, we take a piece of gum from the palate. Then, we place it on the area where you lack gum tissue, after preparing a bed. This method, the oldest, is simple to perform. However, it has several drawbacks. Leaving an open wound on the palate creates post-operative pain. The grafted gum, although solid, does not cover the recessions well and often has an unattractive whitish color.
The Tunneling technique for connective tissue graft
For this more sophisticated technique, we take only a thin layer of the internal part of the gum from the palate or the wisdom tooth area. The harvesting from the palate is done with a single incision, leaving the palate almost intact and protected for healing. Then, we slide the graft under the gum, using sutures, in the area where you lack gum tissue, after preparing a tunnel with micro-instruments.
Although more technical, this method has many advantages. The harvesting area on the palate remains protected. The grafted gum is also covered, providing an aesthetically pleasing appearance immediately after the procedure, which reduces post-operative discomfort. The grafted gum provides thicker tissue, preventing recurrences. The results of covering recessions are high, with about 80% coverage and 50% of patients achieving total coverage. Additionally, the absence of an incision significantly improves the aesthetic aspect.
Tunneling technique for connective tissue graft
Can we use a biomaterial to avoid a graft?
We sometimes use collagen-based substitutes to avoid harvesting. However, their results are significantly inferior to the grafts we harvest.
With the evolution of harvesting techniques and their minimal post-operative effects, we often prioritize harvesting.
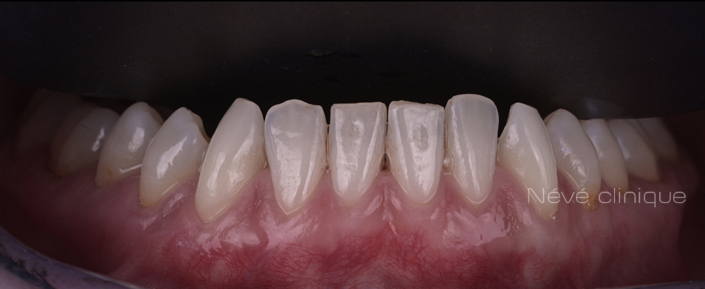
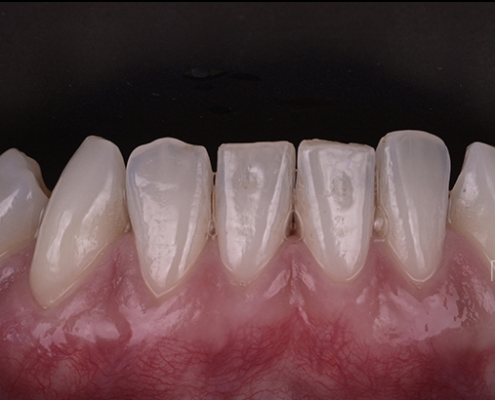
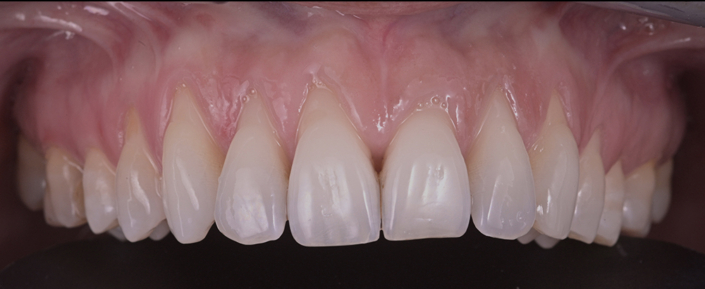
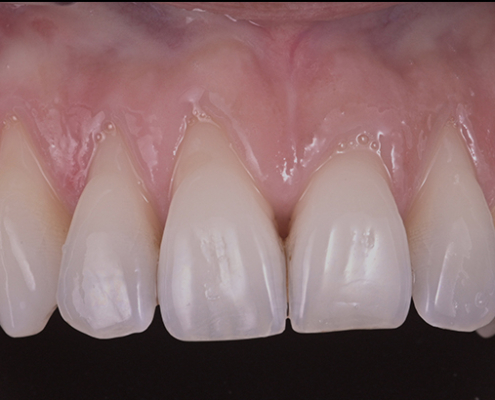
Clinical case #1
Tunneling technique for connective tissue graft
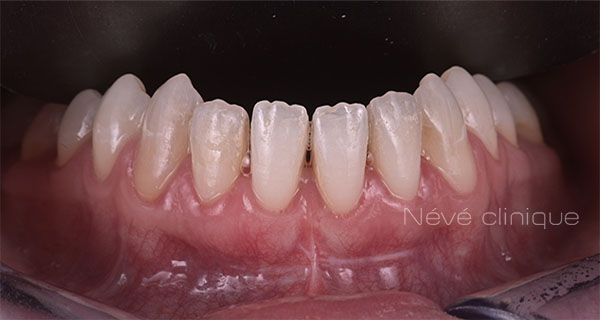
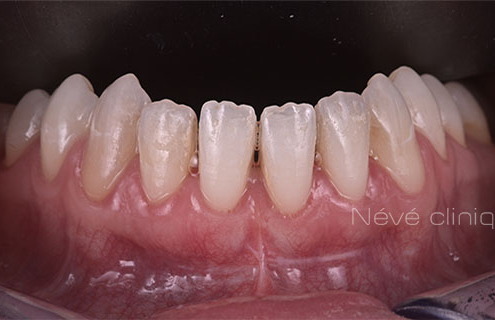
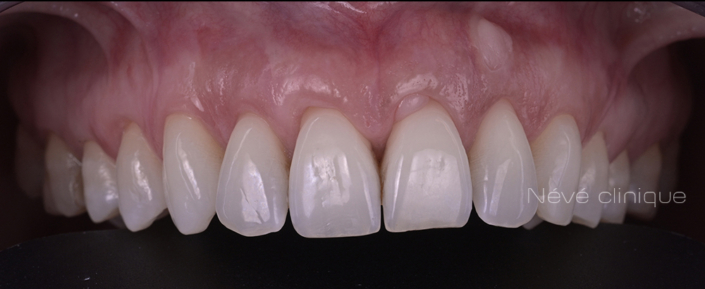
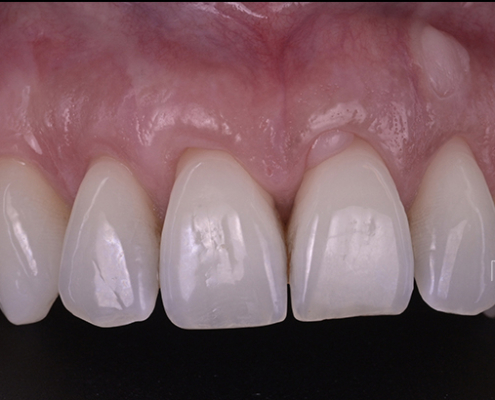
Clinical case #2
Tunneling technique for connective tissue graft
Clinical case #3
Palatal connective tissue graft harvest
Clinical case #4
Tunneling technique for connective tissue graft
Clinical case #5
Tunneling technique for connective tissue graft
Clinical case #6
Tunneling technique for connective tissue graft
Clinical case #7
Tunneling technique for connective tissue graft
How much does a gum graft cost?
For a graft using the most advanced techniques, for half a jaw, the fee is CHF 1753.-
The cost depends on the number of teeth to be treated. Your periodontist will provide an estimate during the first consultation.
Contact us today to learn more about gum grafts. We are here to answer all your questions and provide you with the best possible dental care!